#
Caesar Cipher
A Caesar cipher is a simple substitution method for encoding messages. Letters in the alphabet are shifted with a left or right shift. A Caesar cipher with a right shift of 1 will encode A as B. A left shift of -3 will encode E as B. The Caesar cipher is named for Julius Caesar, who used an alphabet where decrypting would shift three letters to the left.
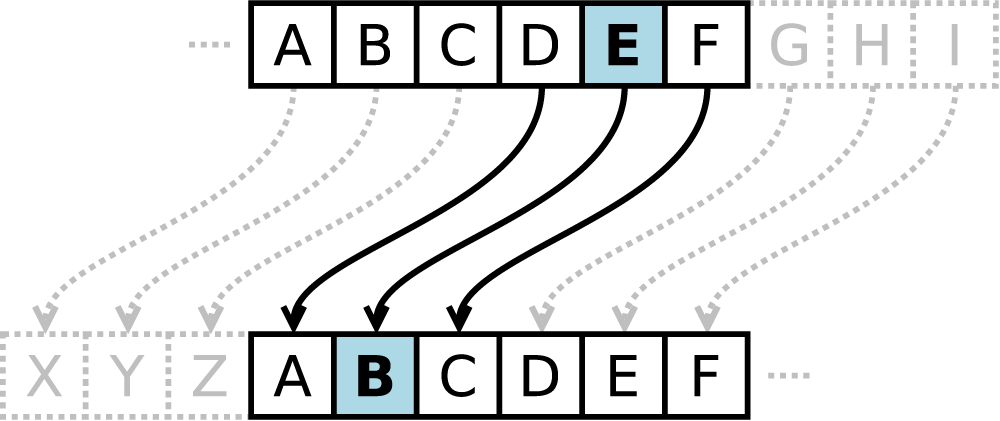
To encrypt plain text we need 2 input variables:
- A String, our plain text message
- An Integer between 0-25 (alphabet has 26 characters)
The first step is to create out input variables on the bottom of our script. Then we print our encrypted message to the console.
text = input("Input Text: ")
shift = input("Shift key (number): ")
print("Cipher: " + encrypt(text,shift))After that we declare out encrypt function, and an empty variable called result which contains our encrypted message. We will use the input of text and shift in our function.
def encrypt(text,shift):
result = ""Now we can create a for loop which will transform our input String into an encrypted message.
for i in range(len(text)): # for each character in our input String text
char = text[i]
if (char.isupper()): # if char is uppercase, 65 = A in the ascii table
result += chr((ord(char) + int(shift) - 65) % 26 + 65)
elif char.find(" ") != -1: # elseif char is a space, remain a space
result += " "
else: # char is lowercase, 97 = a in the ascii table
result += chr((ord(char) + int(shift) - 97) % 26 + 97)
return result # print combined result to consoleFull script:
def encrypt(text,shift):
result = ""
for i in range(len(text)):
char = text[i]
if (char.isupper()):
result += chr((ord(char) + int(shift) - 65) % 26 + 65)
elif char.find(" ") != -1:
result += " "
else:
result += chr((ord(char) + int(shift) - 97) % 26 + 97)
return result
text = input("Input Text: ")
shift = input("Shift key (number): ")
print("Cipher: " + encrypt(text,shift))